The realm of quantum mechanics is a fascinating domain that challenges our understanding of reality.
At its core, quantum mechanics deals with the behavior and interaction of particles at the smallest scales of existence.
One of the most intriguing aspects of this field is quantum object interaction, where particles such as photons, electrons, and atoms interact in ways that defy classical logic.
In this article, we delve deep into the concept of quantum object interaction, its principles, implications, and the technologies it enables.

What Is Quantum Object Interaction?
Quantum object interaction refers to the phenomena that occur when quantum particles influence each other’s states.
Unlike macroscopic objects that follow classical physics, quantum objects exhibit unique behaviors such as superposition, entanglement, and wave-particle duality.
These interactions are governed by the principles of quantum mechanics, which are encapsulated in the mathematical framework of wave functions and operators.
A fundamental principle of quantum mechanics is that particles exist in probabilistic states until observed.
For example, an electron does not occupy a single position; instead, it exists in a cloud of probabilities.
When two quantum objects interact, their wave functions become entangled, leading to correlations that persist even across vast distances.
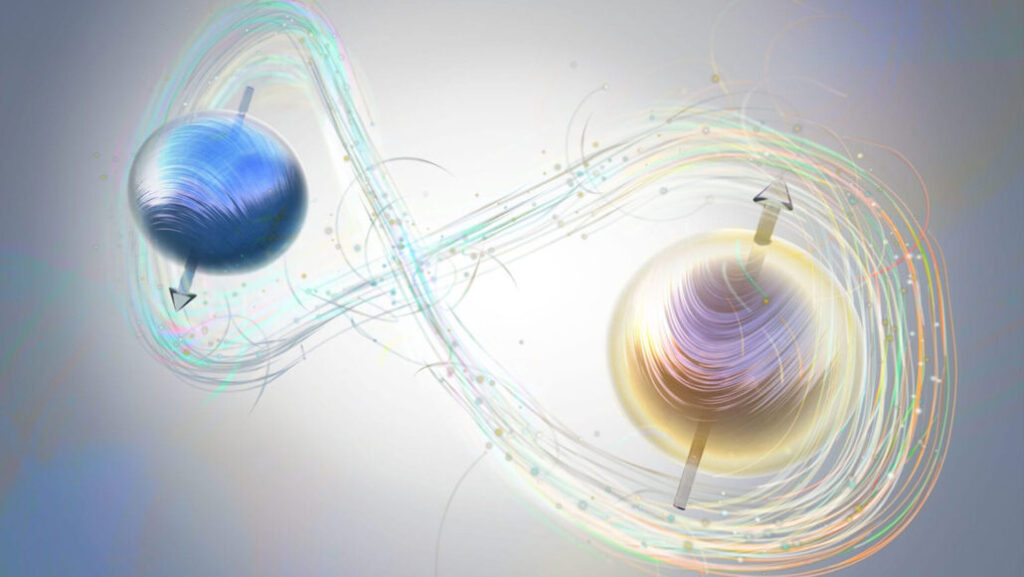
Key Principles of Quantum Object Interaction
▪️Superposition Superposition allows quantum objects to exist in multiple states simultaneously. For instance, a quantum particle can spin up and down at the same time until a measurement collapses it into one definite state. This principle plays a crucial role in quantum computing, where qubits can perform complex calculations faster than classical bits. |
▪️Entanglement Quantum entanglement occurs when two particles become linked such that the state of one instantly influences the state of the other, regardless of the distance between them. This “spooky action at a distance,” as Einstein described it, has profound implications for quantum communication and cryptography. |
▪️Wave-Particle Duality Quantum objects exhibit both particle-like and wave-like behavior depending on how they are observed. This duality is exemplified by the famous double-slit experiment, where photons or electrons create interference patterns characteristic of waves but also behave as discrete particles when measured. |
▪️Decoherence Decoherence describes the process by which quantum systems lose their coherence and transition to classical states due to interaction with their environment. Understanding decoherence is vital for developing stable quantum technologies. |
How Quantum Object Interaction Shapes Reality
Quantum object interactions are the foundation of many phenomena that underpin the universe.
These interactions determine the properties of matter, the behavior of light, and even the mechanisms behind chemical reactions.
In condensed matter physics, the interactions between electrons give rise to properties like superconductivity and magnetism.
Similarly, in quantum field theory, particle interactions explain fundamental forces such as electromagnetism and the strong nuclear force.
One notable application of quantum object interaction is in the field of quantum chemistry.
Here, the interactions between atoms and molecules are modeled using quantum mechanics to predict chemical behaviors with unprecedented accuracy.
This knowledge is critical for designing new materials, drugs, and sustainable energy solutions.

Practical Applications of Quantum Object Interaction
The study of quantum object interaction is no longer confined to theoretical physics; it is driving advancements in technology that promise to revolutionize multiple industries. Some key applications include:
| ▪️Quantum Computing Quantum computers leverage the principles of superposition and entanglement to perform computations that are infeasible for classical computers. These machines excel at solving problems in optimization, cryptography, and complex simulations. For example, they can model molecular interactions for drug discovery or optimize supply chains for maximum efficiency. |
| ▪️Quantum Cryptography Quantum key distribution (QKD) uses the principles of quantum mechanics to create secure communication channels. Any attempt to intercept quantum keys disrupts their states, alerting the communicators to potential eavesdropping. This makes QKD a cornerstone of next-generation cybersecurity. |
| ▪️Quantum Sensors Quantum sensors exploit the sensitivity of quantum states to external forces, enabling ultra-precise measurements of time, gravity, magnetic fields, and more. These sensors are invaluable for applications ranging from medical imaging to navigation in environments where GPS signals are unavailable. |
| ▪️Quantum Communication Quantum entanglement is being harnessed to develop communication networks that are inherently secure and faster than current technologies. Quantum internet prototypes are already demonstrating the potential for long-distance quantum communication. |
| ▪️Advanced Materials By understanding and manipulating quantum object interactions, researchers are developing materials with novel properties, such as high-temperature superconductors, quantum dots for displays, and metamaterials for controlling electromagnetic waves. |
Challenges in Studying Quantum Object Interaction
While quantum mechanics has made significant strides, studying quantum object interaction presents formidable challenges:
- Complexity Quantum systems are inherently complex, and their behavior is difficult to predict due to the probabilistic nature of quantum mechanics.
- Decoherence Maintaining quantum states is challenging because interactions with the environment cause decoherence, disrupting the delicate quantum states.
- Scalability Scaling quantum technologies, such as quantum computers, requires overcoming technical hurdles like error correction and qubit coherence.
- Resource Intensiveness Simulating quantum interactions requires significant computational resources, even with advanced algorithms and high-performance computing.
The Future of Quantum Object Interaction
The field of quantum mechanics is still in its infancy compared to classical physics. However, the rapid advancements in technology and research are pushing the boundaries of what is possible. In the coming decades, we can expect:
🔘 Enhanced Quantum Computing: More powerful quantum computers capable of tackling real-world problems. 🔘 Quantum Networks: Fully functional quantum communication networks that redefine data security and transmission. 🔘 Breakthroughs in Physics: Deeper understanding of quantum gravity and the unification of quantum mechanics with general relativity. 🔘 Quantum AI: Integration of quantum computing with artificial intelligence to unlock new levels of machine learning and data analysis. |
Conclusion
Quantum object interaction is a cornerstone of quantum mechanics, offering profound insights into the nature of reality. From its theoretical foundations to its practical applications, this field is reshaping science and technology.
As researchers continue to unravel its mysteries, the implications for computing, communication, and material science are boundless.
By embracing the quantum revolution, humanity stands on the brink of transformative discoveries that will redefine our understanding of the universe.